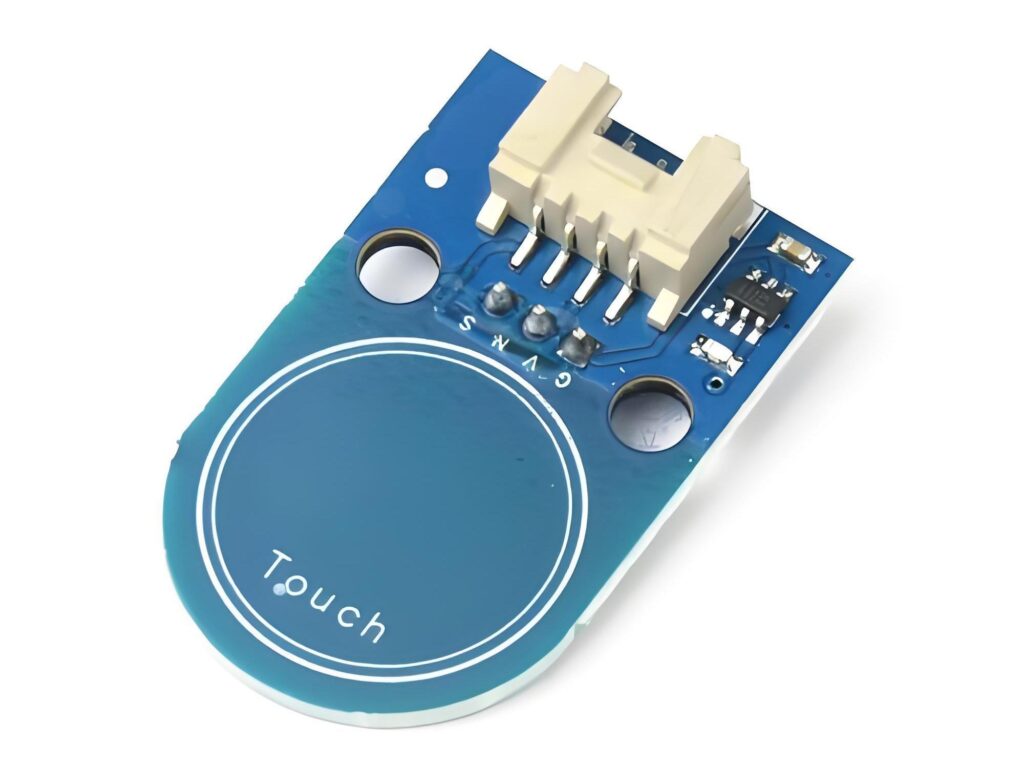
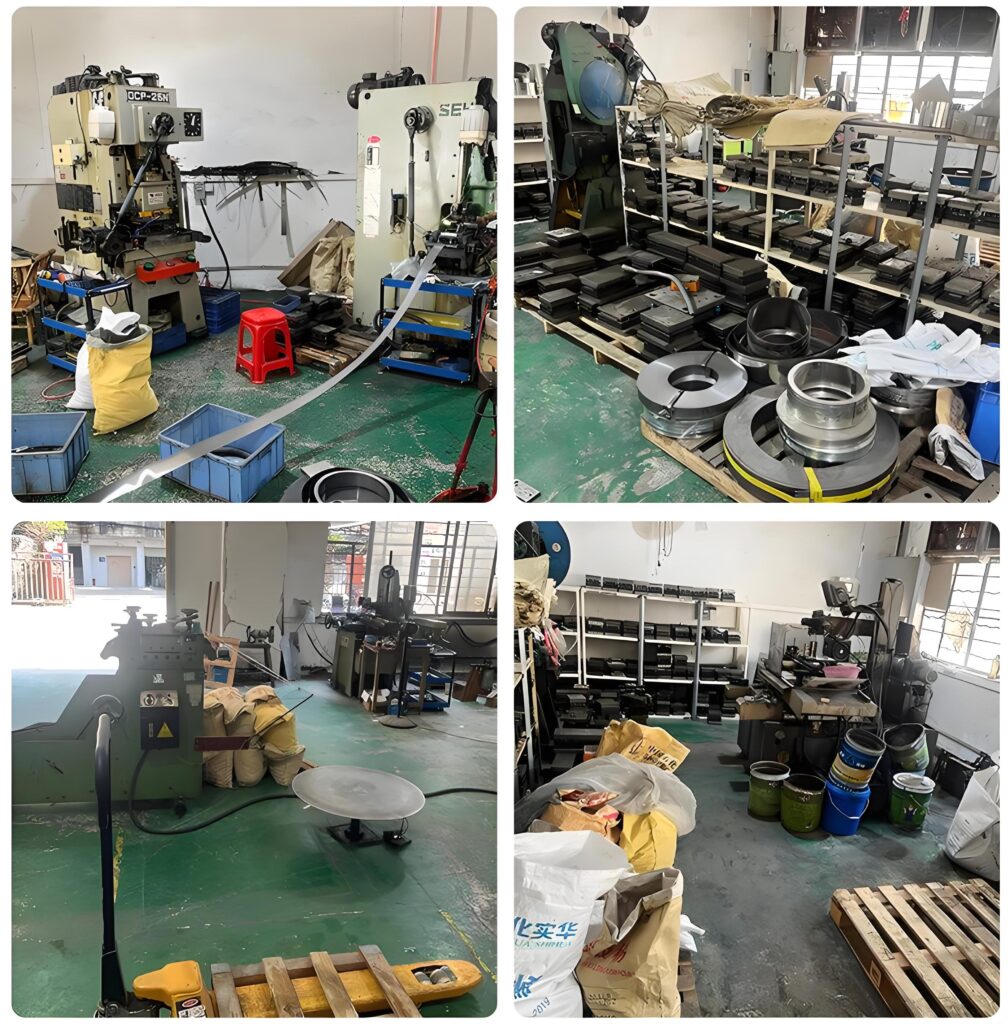
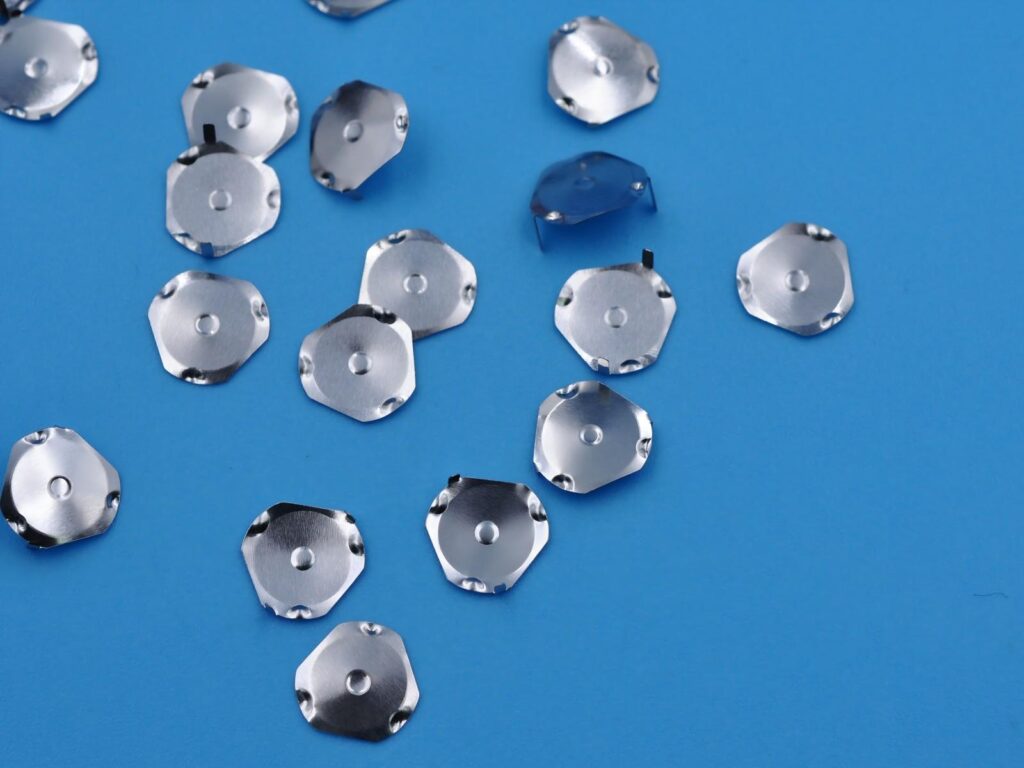
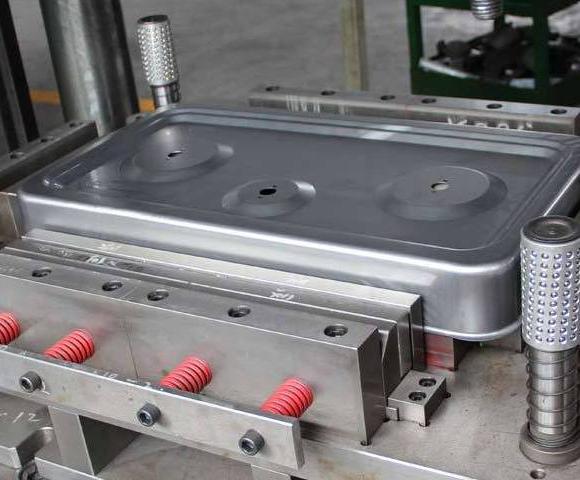
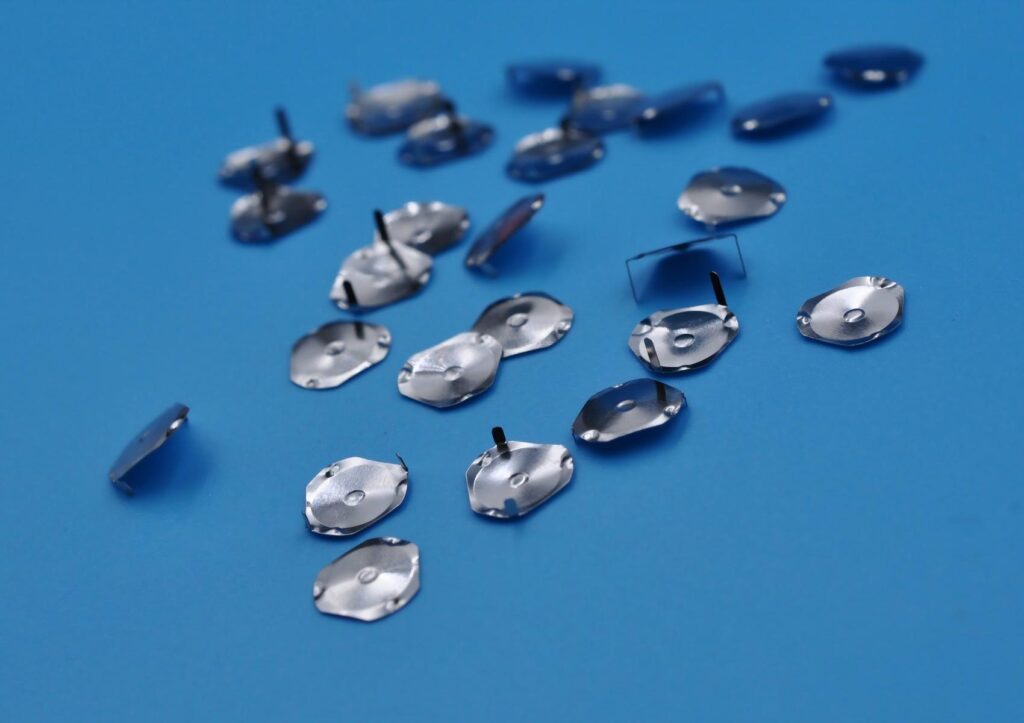
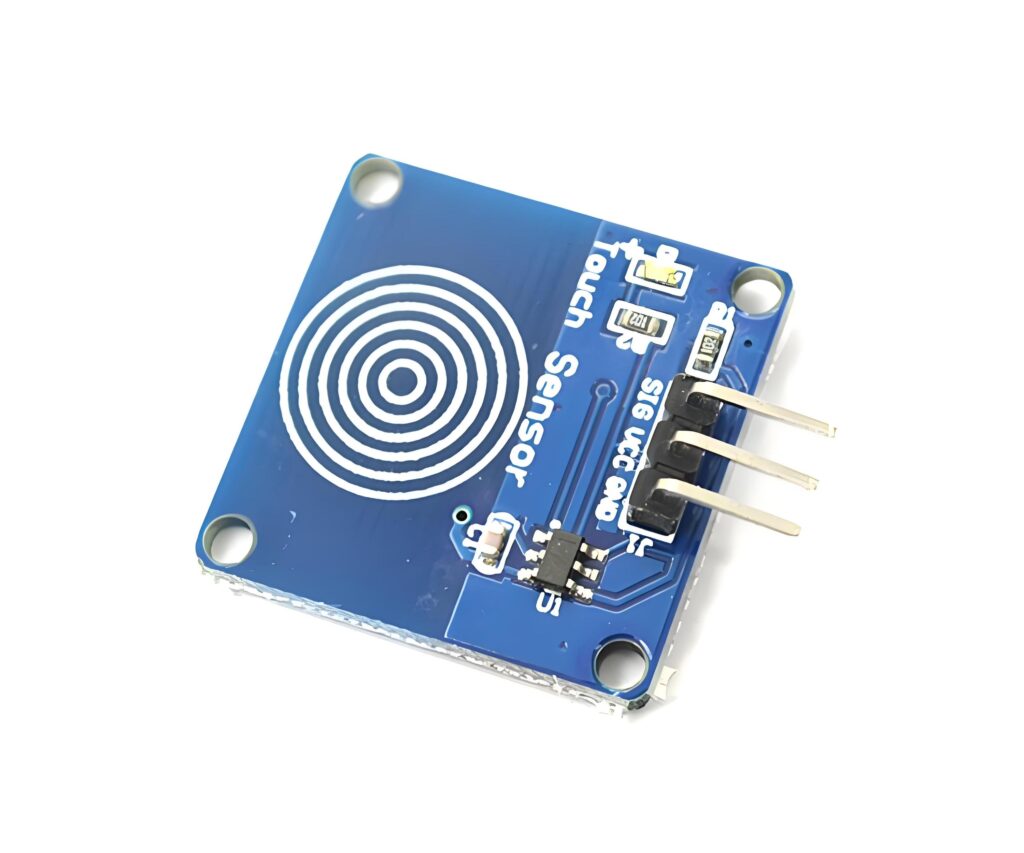
Capacitive switch technology is based on the principle of capacitive sensing and can detect human approach or touch. It monitors the capacitance change through the sensor electrode and triggers the switch when the human body approaches. Capacitive touch switches are commonly used in mobile phones, tablets and other devices, and can provide intuitive feedback and realize contactless operation. Due to its high sensitivity and strong durability, it is widely used in smart home, industrial control and other fields.
How does a capacitive switch work?
Capacitive switch is a type of electronic touch sensor that detects changes in capacitance to trigger an action. Unlike mechanical buttons, it doesn’t need pressure or movement. All it takes is the touch of a finger.
This touch doesn’t even need to be forceful. Just a light tap or even a close hover can be enough to trigger a response. There’s no wear and tear, no noise, and no bouncing like in traditional switches. The surface can remain flat, seamless, and even hidden behind glass or plastic.
Capacitive switches can be printed on flexible films or embedded under decorative surfaces. That’s what makes them so elegant and functional in modern designs.
How does a capacitive switch work?
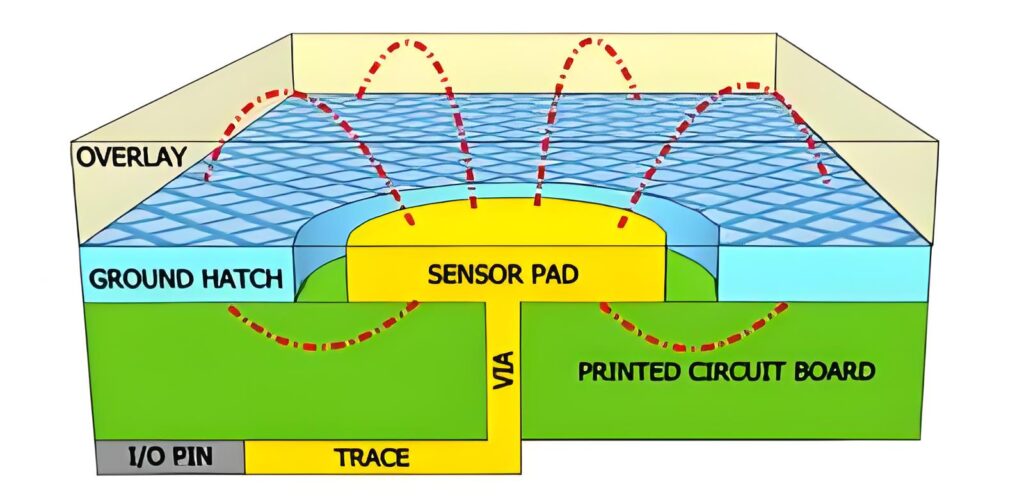
At its core, a capacitive switch detects a shift in electrical charge. The surface of the switch holds an electrical field. When a finger comes close, it disrupts that field. That disturbance changes the capacitance—the ability to store charge—and the system instantly knows you’ve made contact.
Human skin conducts electricity slightly, enough to influence the switch’s sensitive circuits. No springs, no levers. That’s why these switches last longer and require almost no maintenance.
What is a capacitive touch switch sensor?
Capacitive touch switch sensor is the heart of the switch. It’s the part that detects when and where you touch.
These sensors can come in different forms—etched onto a circuit board, printed on a flexible film, or integrated into glass or plastic surfaces. Some sensors are designed for single touches, while others can detect gestures, multi-touch inputs, or even proximity.
They are precise, fast, and reliable. They allow for smooth user experiences and eliminate the frustration of buttons that don’t respond. Sensors can also be tuned for different levels of sensitivity, making them suitable for all types of applications.
In smart homes, cars, medical devices, and wearable tech, capacitive touch switch sensors bring a premium feel and intuitive control.
Where is capacitive switch technology used?
Capacitive switch technology is used everywhere. It’s not just for phones or tablets. Today, it appears in home appliances, industrial machinery, medical devices, automotive dashboards, vending machines, and more.
You’ll find it in:
- Smartphones: Every touch on your phone screen uses capacitive technology.
- Kitchen appliances: Microwaves and ovens with touch panels often rely on capacitive switches.
- Elevators: Modern elevator panels often use capacitive touch sensors.
- Medical equipment: Sterile environments need smooth, wipeable surfaces, which capacitive switches provide.
- Automotive interiors: Sleek car controls now avoid mechanical buttons in favor of capacitive panels.
- Fitness gear: Touch-sensitive buttons are showing up in wearables and exercise machines.
The technology is flexible and can be used on flat, curved, rigid, or flexible surfaces.
Why choose a capacitive touch switch over mechanical?
Capacitive touch switches bring a long list of advantages. They look better, feel better, and work better in many ways.
- No moving parts: Less chance of failure, no mechanical fatigue.
- Seamless design: Perfect for sleek, minimalist products.
- Easier to clean: No crevices or buttons means fewer germs and smoother surfaces.
- Longer life: Outlasts mechanical switches in both function and form.
- Fast response: Instant reaction with just a tap.
- Silent operation: No click sounds, no vibration—just smooth interaction.
- Customizable: Can be printed, shaped, or hidden behind material layers.
These benefits are not just functional. It makes products more desirable, more premium, and more innovative.
How sensitive are capacitive touch switches?
Capacitive touch switches are highly sensitive—but in a good way. They can detect a light finger tap or even proximity, depending on the configuration.
Advanced systems even detect gestures, like swipes and pinches. Some can even differentiate between touch intensity levels. No accidental triggers. No missed touches. Just smooth, intelligent response every time.
Is capacitive touch technology waterproof?
Yes, capacitive touch technology can be made waterproof. Because there are no moving parts, the switch can be fully sealed behind a protective layer.
Designers often use glass, polycarbonate, or acrylic overlays. These are tough, transparent, and easy to seal. With the right materials, the switch can resist water, dust, oil, and even chemicals.
That’s why you’ll find capacitive switches in outdoor equipment, marine controls, and food processing tools. Even when it rains or the area is washed down, the switch stays protected and working.
Some designs work even when the surface is wet or when the user wears gloves. That makes them perfect for environments where traditional buttons fail.
How do you install a capacitive touch switch?
Installing a capacitive touch switch is simple compared to mechanical designs. The switch is often a flat circuit or sensor sheet. You place it behind a panel, connect it to the control board, and it’s ready.
Here’s a basic idea:
Prepare the surface: Glass, plastic, or film can be used.
Position the sensor: It sticks or mounts behind the surface.
Connect to a controller: This reads the touch and sends signals.
Test the switch: Make sure sensitivity and area match your needs.
Seal the unit: For waterproof or dustproof protection.
You don’t need deep enclosures or mechanical supports. The design stays thin and light. This is great for modern devices that require a slim profile.
Conclusion:
Capacitive switch technology is fast, clean and reliable. With no moving parts, it is more durable than traditional switches. The smooth, sealed surface is easier to clean and perfect for stylish designs.
From smartphones and appliances to medical tools and industrial machines, capacitive switches are everywhere. They sense your touch instantly and offer a premium feel. Whether you need beauty, performance, or durability—this technology delivers it all.
Want to know more about how capacitive switch technology can transform your product? Contact us at sales@metal-domes.com