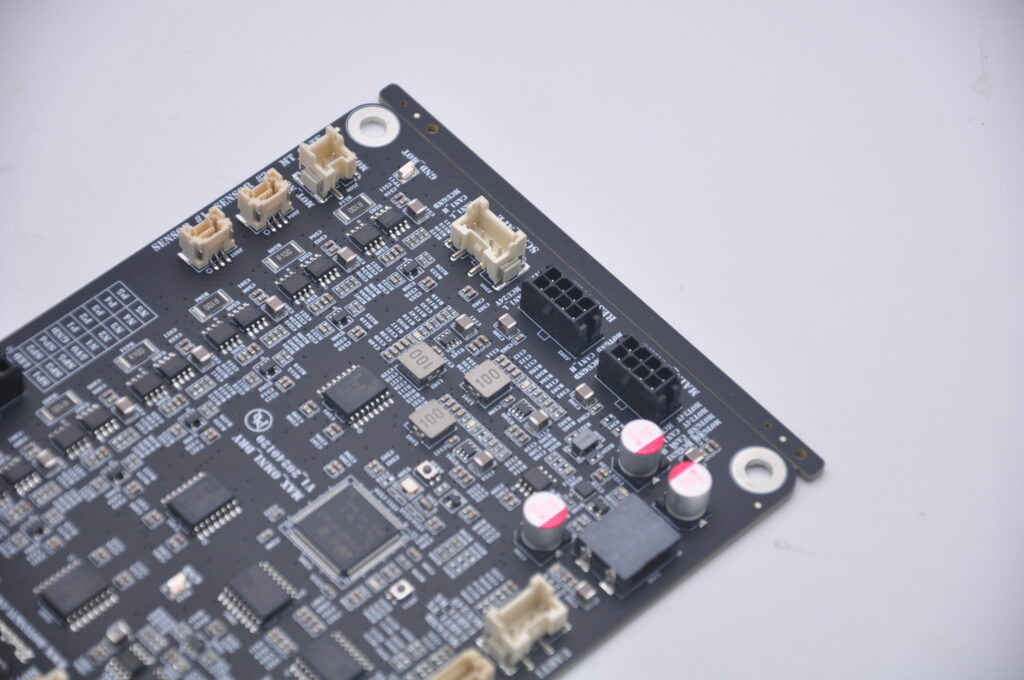
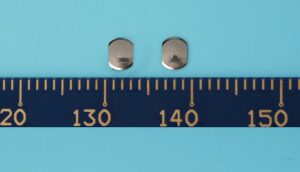
SMT electronic components are compact parts designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board without using traditional leaded pins. These components make modern electronics smaller, faster, and more reliable because they sit close to the PCB and create stable electrical connections.
What Is SMT in Manufacturing?
SMT stands for Surface Mount Technology. It is a process used to place electronic components directly on the surface of a PCB. This technology replaces the older method where parts were inserted through holes. SMT makes the entire assembly flow simpler, faster, and more stable. It also supports higher component density, which means more function in less space.
Many manufacturers prefer this method because it allows automation. That automation delivers consistency and strong quality control. Because of this, SMT helps electronic products reach a higher level of performance and reliability. SMT also reduces the chance of manual mistakes and keeps the production line efficient.
More importantly, SMT aligns with the demand for smaller and lighter devices. From smartphones to medical wearables, SMT enables refined designs without losing power.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SMT
SMT offers many impressive advantages.
- First, it allows high-speed production. Machines can place thousands of components in only one minute. This speed helps companies meet large orders without delays.
- Second, SMT supports small component sizes. These parts help reduce the overall size of the device.
- Third, SMT provides better vibration resistance because parts stay close to the PCB surface.
- Another advantage is improved electrical performance. Shorter leads reduce parasitic inductance, which helps high-frequency designs operate smoothly. That is important for RF, high-speed digital, and communication products.
- SMT also lowers assembly cost in many cases because automated lines reduce labor.
However, SMT still has a few limitations.
The welding process for repairing very small parts requires precise temperature control. Some components may not support SMT because they need strong mechanical strength. Even so, these limitations affect only a small part of the industry. For most designs, the advantages dominate the disadvantages by a wide margin.
What Are SMT Electronic Components?
SMT electronic components are parts made specifically for surface mounting. They come in many shapes and functions. Resistors, capacitors, diodes, ICs, and transistors are the most common types. These components are placed on copper pads instead of being inserted through drilled holes.
These components stay on the board through solder paste. During reflow soldering, the paste melts and forms strong joints. Because these components are small and efficient, engineers can design compact devices without losing performance.
There are two broad categories of SMT electronic components. One group is passive components. These include resistors and capacitors. They help control signals, filter noise, or adjust power levels. The second group includes active components. These include ICs, transistors, and regulators. They manage switching, logic control, power control, and other advanced tasks.
Together, these components create the complete electronics environment inside every device we use today. Their size, speed, and reliability make them the preferred option for modern manufacturing lines.
Difference Between SMT and SMD Components
SMT and SMD sound similar, but they have different meanings. SMT is the process. SMD refers to the component. SMT describes the assembly technology used to mount parts on a PCB. SMD describes the physical part designed for that technology.
For example, a capacitor in 0402 size is an SMD part. Placing that capacitor on the PCB using reflow soldering is SMT.
Understanding the difference also helps avoid mistakes in design files and component selection. This simple clarification helps communication flow better across teams, especially during mass production.
What Is the Difference Between PCB and SMT?
PCB refers to the printed circuit board. It is the physical board made of layers, copper traces, and insulating materials. SMT refers to the technology used to mount components on this board.
A PCB can exist without SMT if it is still bare. But SMT cannot exist without a PCB because the board acts as the foundation of the assembly. During SMT assembly, components attach to the PCB with solder paste.
How Does SMT Work?
The SMT process follows a clear sequence. Each stage contributes to strong, stable, and repeatable assembly. The most common steps include:
- 1. Solder Paste Printing
A stencil covers the PCB. A machine presses solder paste onto exposed pads. This step requires accuracy because any misalignment can affect the next steps.
- 2. Component Placement
Machines pick up SMD components and place them on the solder paste. The paste holds the parts in place before reflow.
- 3. Reflow Soldering
The board enters a reflow oven. Temperature rises in stages to melt the solder paste. When it cools, the solder hardens and creates strong electrical joints.
- 4. Inspection
Many factories use SPI and AOI systems. SPI checks paste volume. AOI checks component placement and solder quality.
- 5. Testing
Functional tests ensure the board works properly. Some products require in-circuit testing, while others require burn-in tests for stability.
This full flow is fast, reliable, and ideal for mass production. SMT gives factories the power to produce thousands of boards per day while maintaining high quality.
What Are the Top 10 Popular SMT Machine Brands?
Many manufacturers dominate the SMT equipment market. These brands offer trusted performance, high-speed production, and stable placement accuracy. Here are ten brands that many factories rely on worldwide:
- Panasonic: A leader in speed and long-term reliability. Known for high-end placement lines.
- Yamaha: Offers flexible platforms and strong software integration.
- Fuji: Popular for precision and durability. Suitable for mid to high-volume production.
- JUKI: Affordable and widely used for cost-efficient manufacturing.
- ASM/Siemens: Premium machines designed for advanced and demanding assembly.
- Samsung/Hanwha: Strong performance with competitive pricing and smart automation.
- Mycronic: Excellent for prototypes, high-mix, or low-volume manufacturing.
- Universal Instruments: Known for rugged build and long service life.
- Nordson: Specializes in dispensing and coating machines essential to SMT lines.
- Koh Young: The global leader in SPI and AOI inspection systems.
These brands support strong production outcomes because they deliver stability and accuracy. They also help factories reduce costs and improve throughput.
What Is the SMT Used For?
SMT finds use in almost every electronics sector. It supports consumer electronics, industrial control, medical devices, automotive electronics, and aerospace systems. Almost all modern PCBs rely on SMT because it improves electrical performance and production efficiency.
SMT is also essential in products that need compact size. Smartphones, laptops, and wearables depend heavily on SMT components. Other fields like automotive ADAS, medical imaging systems, and aerospace avionics lean on SMT because it provides vibration resistance and long-term stability.
In short, SMT drives innovation because it enables smart products to become smaller, faster, and stronger.
Conclusion:
SMT electronic components shape modern electronics with strength, speed, and precision. They help manufacturers build compact devices with powerful performance. They make production stable and allow factories to scale with confidence.
If you need stable and professional SMT assembly or PCB manufacturing support, Best Technology is ready to help. For inquiries or quotes, please contact: sales@metal-domes.com