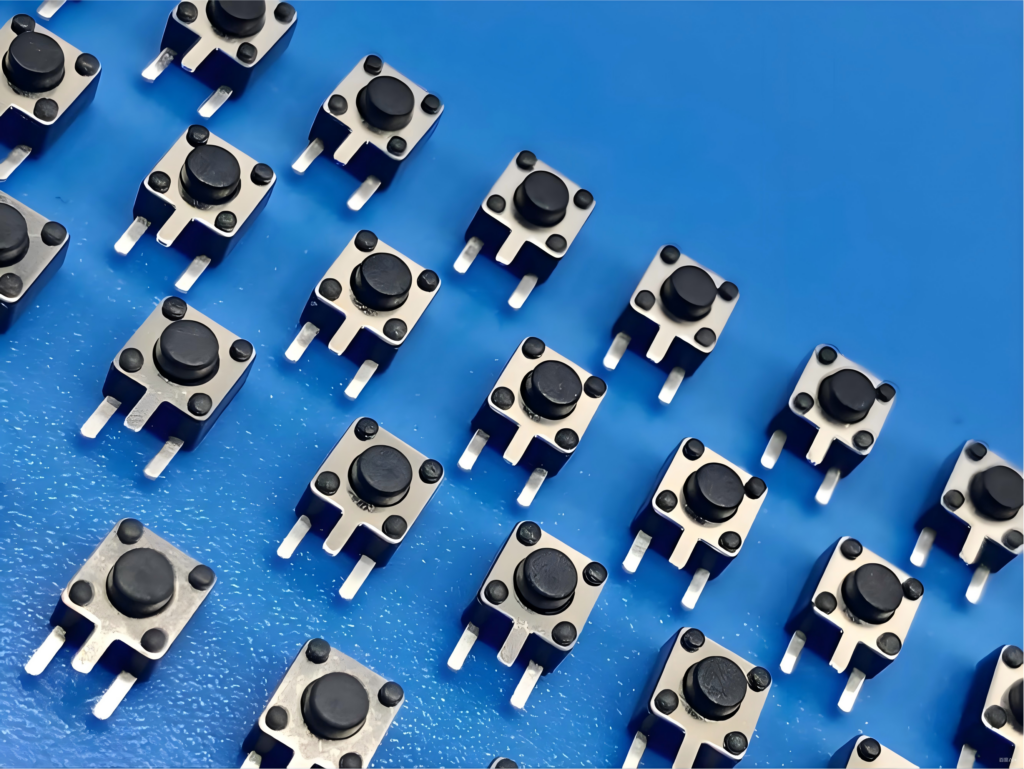
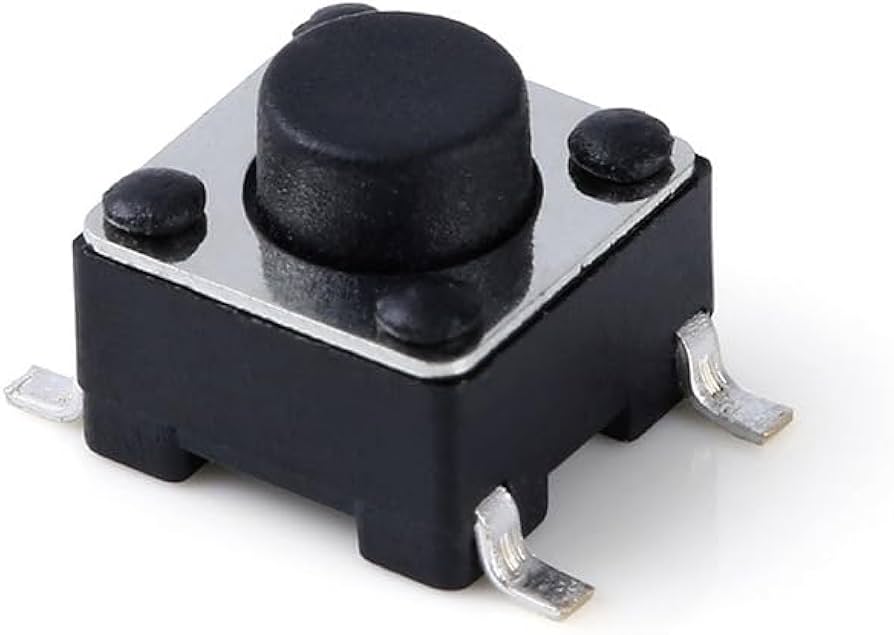
Push switch SMD is a compact, momentary mechanical switch designed to be soldered directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board. It activates when pressed and returns to its original state when released, making it ideal for short-duration inputs such as power, reset, mode selection, or user commands in electronic products.
What is an SMD switch?
Push switch SMD is a compact electrical switch designed for surface mounting on a printed circuit board. Instead of using through-hole pins, the terminals sit directly on copper pads. This structure allows automated placement and reflow soldering, which aligns well with modern electronics production.
In practical terms, an SMD push button switch enables momentary or maintained contact when pressed. It is widely used for power keys, reset functions, mode selection, and user input. You see it in consumer devices, industrial controls, medical electronics, and compact IoT products. The small footprint supports dense layouts, while consistent solder joints support stable electrical performance.
What does SMD stand for?
SMD stands for Surface Mount Device. The term describes components mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB rather than inserted through drilled holes.
This mounting method changed electronics manufacturing. It allowed smaller boards, shorter signal paths, and faster assembly. With SMD parts, circuits became lighter and more compact without losing function.
A push button switch in SMD form benefits from this approach. The electrical path stays short. Mechanical stability improves when pads are designed correctly. Assembly time drops. Cost control becomes easier.
What are the two types of push button switches?
Push button switches generally fall into two functional categories. Each type serves a clear purpose and supports different user interactions.
- Momentary push button switches
These switches only stay active while pressed. Once released, the circuit returns to its original state. Most SMD tactile push button switches fall into this category. They are common for reset buttons, keyboard inputs, and menu navigation.
- Latching push button switches
These switches maintain their state after pressing. One press turns the circuit on. Another press turns it off. Latching styles appear less often in SMD form but still exist for specialized designs.
Choosing between these types depends on how the user interacts with the device. For compact electronics, momentary SMD push switches dominate due to simplicity and reliability.
What is a DPDT switch?
A DPDT switch stands for Double Pole Double Throw. It controls two independent circuits at the same time, with each circuit able to connect to one of two outputs.
In simple terms, one action changes two signal paths. This design supports polarity reversal, signal routing, or mode switching. While DPDT structures appear more often in slide or toggle switches, they can also apply to push button designs in some assemblies.
In SMD applications, DPDT push switches are less common due to space limits. Yet they remain useful when circuit control must stay compact while handling multiple signals.
Can push buttons be customized?
Yes, push button switches can be customized in several meaningful ways. Customization allows designers to match both electrical and mechanical requirements without compromise.
Common customization options include:
- Actuation force to adjust tactile feel
- Cap shape and height to match enclosure design
- Terminal layout for specific PCB footprints
- Contact material to improve conductivity or durability
- Operating life rating for long-term reliability
For SMD push button switches, customization often focuses on size, force, and mounting pad geometry. These details help ensure smooth assembly and consistent user experience. Custom solutions also help products stand out while maintaining electrical stability.
What is the life expectancy of a pushbutton?
The life expectancy of a push button switch is measured in cycles. One cycle equals one press and release. For SMD tactile push button switches, ratings often range from one hundred thousand to several million cycles.
Several factors influence lifespan. Actuation force plays a role. So does contact material. Environmental exposure also matters. Dust, moisture, and vibration can reduce service life if not addressed during design.
In controlled environments, a well-designed push switch SMD can operate reliably for years. For mission-critical electronics, designers select switches with higher cycle ratings and stable materials.
What are the four types of push pull switches?
Push pull switches differ from standard push buttons in operation. They involve two distinct motions.
The four common types include:
- Push-push: press once to activate, press again to release
- Push-pull: push to engage, pull to disengage
- Momentary push-pull: active only while held
- Locking push-pull: stays engaged until manually released
In compact electronics, these mechanisms often translate into latching or momentary logic using tactile SMD push switches combined with circuit control. The physical concept remains relevant even when the form factor changes.
Does a push switch have polarity?
Most mechanical push button switches do not have polarity. They act as simple contacts that open or close a circuit. Current can flow in either direction.
However, polarity becomes relevant when additional elements exist. If the switch includes an LED, internal diode, or specific signal conditioning, polarity matters. In such cases, terminals are clearly marked.
For standard SMD push button switches without integrated electronics, polarity is not a concern. Designers focus instead on contact rating, footprint accuracy, and solder joint reliability.
What are common push button problems?
Push button switches are reliable components, yet issues can arise over time or due to poor design choices.
- Contact wear from repeated use
- Poor solder joints due to incorrect reflow profiles
- Mechanical fatigue from excessive actuation force
- Contamination from dust or moisture
Most of these issues are preventable. Proper footprint design improves solder quality. Correct force selection reduces wear. Sealed switch options protect against environmental exposure.
Conclusion:
A push switch SMD is a compact, surface-mounted solution for user input and circuit control. It supports modern PCB assembly, offers flexible design options, and delivers dependable performance across industries.
For technical support, samples, or custom solutions, please contact sales@metal-domes.com