What Is an SMD Switch?
An SMD switch (Surface Mount Device switch) is a compact electrical switch designed for surface mounting directly onto a PCB. Unlike traditional through-hole switches, which require drilling holes for leads, SMD switches sit flat on the surface of the board.
These switches are part of a broader class of SMD components, such as resistors, capacitors, and LEDs, all designed to simplify assembly using automated pick-and-place equipment.
SMD switches are available in different forms: SMD push button switches, SMD tactile switches, SMD slide switches, and even SMD toggle switches. Their small footprint makes them perfect for devices where space is limited but performance can’t be compromised.
In short, SMD switches are where precision meets practicality — compact, reliable, and essential for modern PCB assemblies.
What Is SMD vs SMT?
It’s easy to confuse SMD with SMT, but the two are not the same thing.
SMD (Surface Mount Device) refers to the actual component — in this case, the switch. SMT (Surface Mount Technology), on the other hand, describes the manufacturing process that mounts those components onto the circuit board.
So when we say SMD switch, we’re talking about the hardware itself — the physical button or toggle. When we refer to SMT, we’re talking about how it’s placed on the PCB using solder paste and reflow ovens.
Knowing the difference helps you understand what you’re ordering, whether you’re looking for parts or PCB assembly services.
How Does an SMD Switch Work?
At its core, an SMD switch performs a simple task: it opens or closes a circuit. When you press the actuator, it connects two internal contacts, allowing current to pass. When released, the contacts separate, interrupting the flow.
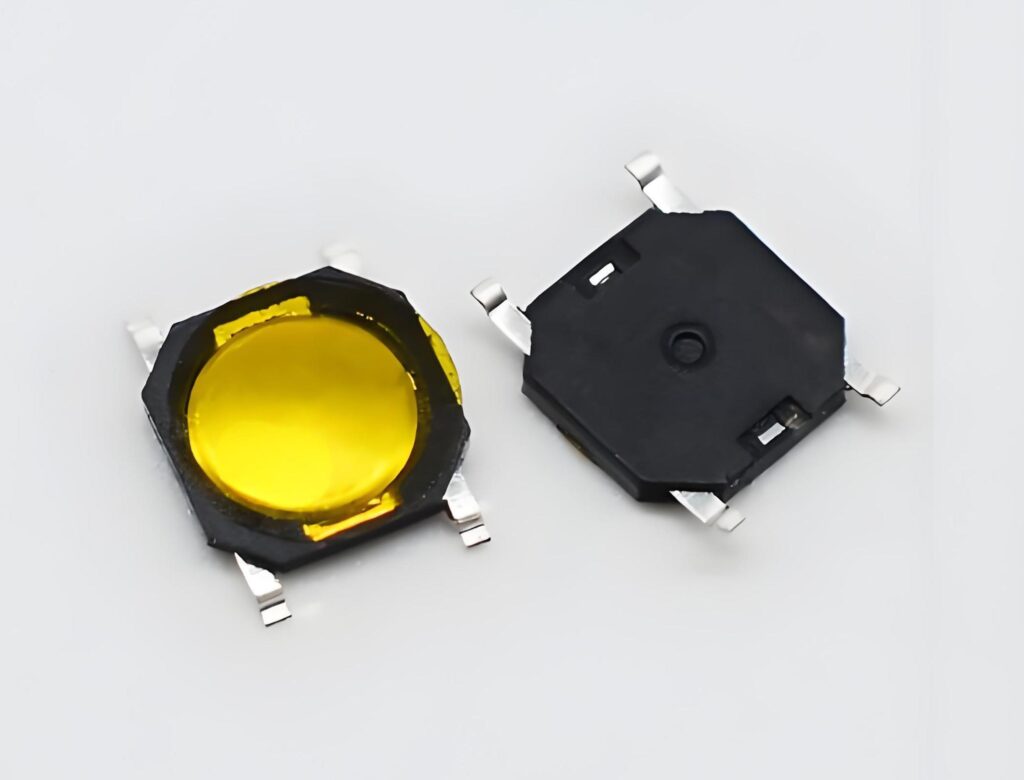
Inside an SMD tactile switch, for example, lies a metal dome that flexes under pressure. This dome provides a distinct “click” feedback — a satisfying tactile response that confirms activation. That’s why it’s often used in keyboards, remotes, and control panels where the user needs feedback.
Some types, like SMD momentary switches, only stay active while pressed, while latching types remain on until pressed again. SMD dome switches are engineered for reliability, typically offering tens of thousands of actuation cycles before wear.
The simplicity of operation, paired with durability and precision, is what makes SMD switches indispensable in compact electronic designs.
What Are the Types of SMD Switches?
The diversity of SMD switches is what makes them so adaptable.
- 1. SMD Tactile Switch
The tactile SMD switch is one of the most widely used types. It’s small, gives a crisp click when pressed, and is perfect for human-machine interfaces. They use a metal dome to provide tactile feedback and ensure consistent electrical contact.
- 2. SMD Push Button Switch
The SMD push button switch operates similarly but may offer a softer touch. It’s used in devices that need frequent pressing, such as keyboards or consumer electronics. Their flat profile fits easily into slim casings, keeping product designs sleek.
- 3. SMD Slide Switch
The SMD slide switch is used to toggle between on/off states by sliding a small actuator back and forth. They’re simple, sturdy, and provide clear visual confirmation of switch position.
- 4. SMD Toggle Switch
The SMD toggle switch offers the traditional lever-style control, allowing users to flip between positions. Though slightly larger than tactile types, they’re used where mechanical durability and clear actuation are vital — such as in test instruments and control systems.
- 5. SMD Dome Switch
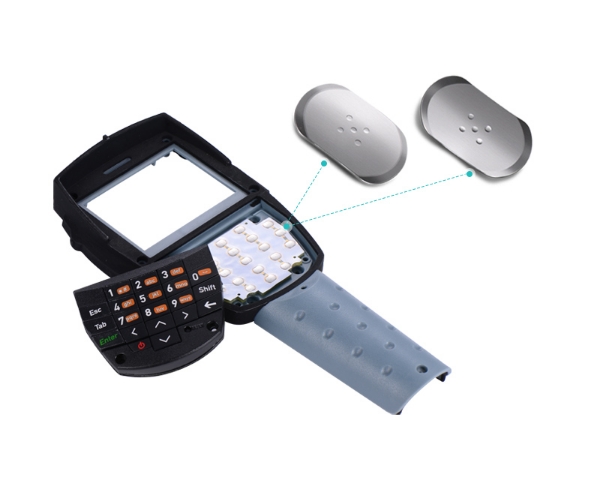
An SMD dome switch integrates a metal dome to provide tactile feedback and contact reliability. These domes are usually made of stainless steel for excellent resilience. They are widely used in SMD switch keyboards, medical instruments, and custom control pads. The dome’s shape and material influence the actuation force and tactile feel, making customization easy.
Each type serves a unique role, but all share one thing: efficient, compact design built for modern PCB assembly lines.
What Are the Advantages of SMD Switches?
When comparing SMD switches to traditional through-hole versions, the benefits are clear — and significant.
- Space Efficiency: SMD switches consume far less board space.
- Automated Assembly Compatibility: Because they are surface-mounted, SMD switches are compatible with automated pick-and-place machines, reducing labor costs and increasing consistency during mass production.
- Electrical Reliability: Shorter lead lengths mean less inductance and resistance, improving signal integrity.
- Aesthetic and Structural Integration: Their low profile contributes to sleek, modern product designs.
- Cost-Effective in Volume: With fewer manual processes and faster production speeds, SMD switches reduce assembly time and overall cost — particularly for large-scale manufacturing.
- Tactile Feedback and Longevity: Tactile SMD dome switches and push button designs provide crisp feedback and consistent feel, even after thousands of cycles.
Altogether, SMD switches are a smart choice when balancing performance, size, and production efficiency.
What Are SMD Switches Used For?
The applications of SMD switches stretch across industries. Their versatility makes them a standard component in many everyday devices.
- In consumer electronics, they’re used in smartphones, tablets, cameras, and wearables to control power, mode, or brightness.
- In automotive systems, you’ll find them in dashboard controls, key fobs, and infotainment systems, where tactile feedback and reliability are critical.
- In industrial and medical equipment, SMD switches handle command inputs, alarms, and control functions with precision and repeatability.
- Even in computing and IoT devices, SMD tactile switches serve as reset buttons, boot controls, or function keys on small circuit boards.
Their compactness and consistency make them an ideal fit for high-density electronic environments where space and reliability both matter.
How to Choose the Right SMD Switches?
Choosing an SMD switch isn’t only about size. Several key parameters influence performance and compatibility. Here’s what you should focus on when making a selection:
- 1. Electrical Ratings
Check the voltage and current specifications first. Exceeding these can shorten switch life or cause failure.
- 2. Actuation Force
The actuation force — typically measured in grams — defines that balance. Too light, and accidental presses happen. Too stiff, and the device feels unresponsive. For example, SMD dome switches can range from 100g to 400g depending on the desired tactile feedback.
- 3. Travel Distance
Travel distance defines how far the button moves before activation. Shallow travel creates quick responses, while longer travel provides a stronger tactile feel.
- 4. Mounting Type and Footprint
Confirm that the switch’s footprint matches your PCB layout. Even a small mismatch can cause assembly issues. Most SMD switches follow standard sizes, but custom layouts may require slight adjustments.
- 5. Environmental Resistance
If the device operates in harsh conditions — such as automotive or outdoor electronics — you’ll need switches rated for dust or moisture protection.
- 6. Operating Life
Every switch has a rated number of cycles. A SMD push button switch may last 100,000 presses, while industrial-grade SMD dome switches can endure millions. Match the life cycle to expected usage frequency.
- 7. Height and Orientation
When designing slim electronics, height matters. Low-profile small SMD switches help maintain a flat surface without sacrificing functionality.
- 8. Aesthetic and Tactile Feel
User experience often defines product quality. Test how the switch feels and sounds. The feedback of an SMD tactile switch can set your product apart, especially in premium electronics.
- 9. Reliability and Brand Quality
Choose switches from trusted manufacturers with proven testing standards. Inferior switches may degrade over time, leading to performance inconsistencies.
By carefully reviewing these factors, you can choose SMD switches that not only fit your design but also enhance it — in function, feel, and longevity.
Conclusion:
SMD switches are compact, efficient, and widely used in today’s electronics. They differ from traditional through-hole switches by mounting directly on PCB surfaces.
At Best Technology, we specialize in SMD dome switches, tactile SMD switches, and custom metal dome arrays for global clients. Our strict quality management system — backed by ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, and AS9100D certifications — ensures every part meets the highest standard.
Selecting the right one requires attention to actuation force, travel, footprint, life cycle, and environmental resistance. Partnering with a reliable supplier like Best Technology ensures your switches perform flawlessly — from prototype to production. Contact: sales@metal-domes.com